The Boom Time: Arabesque Story of the Rise and Rise of Indian Aviation
The history of Indian aviation dates back to Hundred Twelve years, Nine months and Twelve days ago, when on February 18, 1911, at the pious Kumbh Mela time, Henry Piquet transported 6500 mails on a Humber biplane between Allahabad to Naini (6-mile), in what is now known as world’s first airmail service.
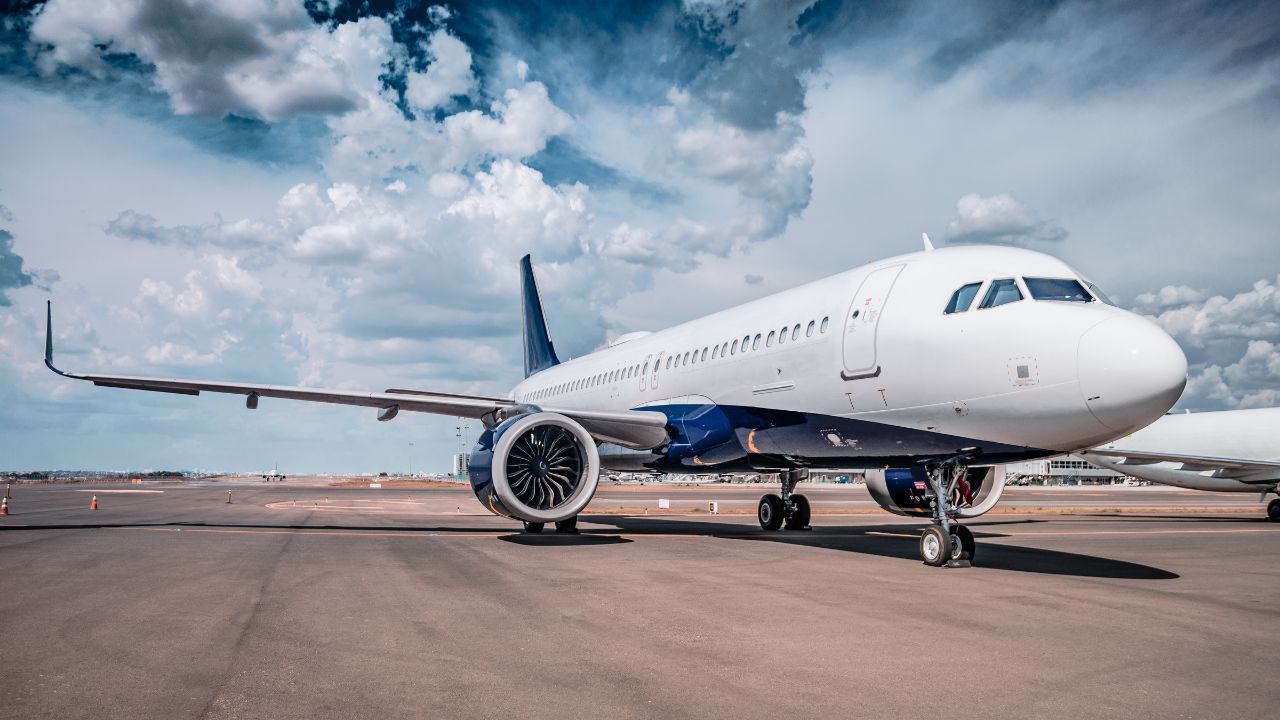

The Rise of Indian Aviation
The history of Indian aviation dates back to Hundred Twelve years, Nine months and Twelve days ago, when on February 18, 1911, at the pious Kumbh Mela time, Henry Piquet transported 6500 mails on a Humber biplane between Allahabad to Naini (6-mile), in what is now known as world’s first airmail service. The first British Indian Government Air Service and Imperial Airways, UK-owned London- Karachi-Delhi international flight commenced operation in December 1912.
The Sobriquet
Nonetheless, the birth, rise and rise of Indian aviation are accredited to the humungous contribution of one India Jehangir Ratanji Dadabhoy Tata (JRD or Jeh), who rightly got him the sobriquet ‘Father of Indian Aviation’. My love for flying got kindled in ‘Jeh’ when 15 after a plane joyride in France. And the rest is history. In February 1929 he became the first Indian to get a pilot license, in 1932 he jumped started aviation in India with his inaugural flight from Karachi to Bombay. Soon he founded a small freight airline that progressed to become a commercial passenger airline. The airline by 1938 was named Tata Airlines running domestic operations to many cities. The airlines played a major role in World War II carrying troops for Britain.
For the Love of Nation
Though Indian aviation has scaled heights in recent decades, the history of aviation in India very much has been the gift of one ‘Jeh’ and one nation builder called-‘House of Tatas, all for the love of the nation. In 1946 Tata Airlines got a new name ‘Air India' and the Indian Government agreed to a contract in 1948 for Air India International Ltd. to run international flights.
Based on a 1952 recommendation of the Planning Commission, in 1953, through an Act of Parliament (the Air Corporations Act) nine privately owners Airlines-Air India, Air India International and their seven smaller siblings (Bharat Airways, Deccan Airways, Himalayan Aviation, Indian National Airways, Kalinga Airlines) were nationalized creating two government monopoly of commanding heights- Indian Airlines and Air India.
Nonetheless, respecting the love of Jeh for the future of aviation in India and recognizing his unparalleled contribution, Prime Ministers from Nehru to Indira Gandhi retained J. R. D. as Chairman of two airlines. Thence came Morarji Desai, who on February 1, 1978, dismissed Chairman Jeh Tata at the pleasure of the President of India from the boards of Air India and Indian Airlines. Indira Gandhi reinstated him on the boards of both airlines in April 1980.
The aviation sector of India got wings in 1994 with the repeal of the ‘Air Corporation Act’ and the country witnessed the birth, growth and biting of the dust of private airlines- Jet Airways, Air Sahara, Modi Luft, Damania Airways, NEPC Airlines, and East-West Airlines. By 1995, private airlines handled more than 10% of domestic routes. As the country entry entered the new millennium India had more than 40 operational airlines big and small, but none survived.
Sooner in 2004, the government granted permission to Indian scheduled airlines with at least five years of continuous service and a fleet of at least 20 aircraft to operate scheduled flights to international destinations. New generation airlines, Vijay Malaya’s blue-eyed King Fisher arrived in 2005, and the real era of budget airlines arrived with Indigo in 2006- though the first budget airlines to arrive were Air Deccan (2003), SpiceJet (2004), Go First 2005). Vistara 50:50 owned by Tatas and SIA entered the fray in 2013 and the latest baby on the block is Alaska Air.
I will return to the spectacular growth of the Indian Aviation sector, a bit later, but suffices to say that despite the superlative growth of the aviation sector, the story of Airlines in India has been one of booms and busts, more headwinds and less tailwinds, with lesser life span and high mortality rate. It has been a classic tale of past imperfect.
Bittersweet Homecoming
After decades of mismanagement, deteriorating services, unquantifiable losses, dwindling market share, and unbearable debt, the congenital twins Indian Airlines and Air India separated and slipped into a coma plagued with terminal malignancy. Then emerged the white knight, the same Tata Group, and after seventy years it was the sweet homecoming of Air India (remerged entity), At the time of homecoming, the State-run Air India was teetering on the brink with its domestic market share shrunk from low 17.3 per cent in 2014 to minuscule 9.6% in 2021.
Duopoly
With Indigo emerging as the leader of the pack with the overwhelming market share and Tatas collapsing three of their airlines (Air India, Vistara and Air Asia) under the Air India brand and others either in disarray or too small or too new to get counted, it is back to square one, a literal duopoly in Indian Aviation- Air India and Indigo. While the Indigo market share is above 60%, Air India Group is back in reckoning with a 27% market share, the two sending other players to the gallows. High mortality and low shelf life of airlines do not bode well for the world one of the fastest-growing aviation markets.
Arabesque, Spectacular, Bejeweled
Amid the story of the boom and bust of airlines, the three adjectives arabesque, spectacular, and bejewelled define the unprecedented growth of aviation in India. Growing at an unprecedented rate, coming from behind the country has become the third-largest domestic aviation market in the world just behind China and the USA and by 2024 is set to surpass the UK as the third-largest air passenger market. Already the Indian aviation sector contributes 5% to the GDP, accounting for 4 million jobs. The gross value-added contribution of Aviation Industry to the country’s GDP exceeds US$ 72 billion.
Domestic air passenger traffic in the first half of the current fiscal year (between April-September) was 75.4 million, year-on-year growth of 20% and 7% higher than pre-COVID levels. As regards the international passenger share of domestic airlines between April-July 2023, it was 9.2 million, a year-on-year growth of 32%, and higher than the pre-COVID levels of 7.2 million. The airlines’ capacity deployment in September 2023 was higher by 10% than that of September 2022.
Over last decade India has been the fastest-growing aviation market fastest-growing market in the world, growing at almost 10 per cent for the last decade, almost 2.5 times the global average. Over the past six years, India’s domestic passenger traffic has grown at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 14.5 per cent, while international passenger traffic has increased by a CAGR of around 6.5 per cent.
Future Perfect- The Pole Position
India, the fastest growing major economy of the world, is on the threshold of becoming the world’s most populous country dethroning China, the third-largest economy by 2028, with a middle class of the size bigger than the USA population with fast-paced growth of discretionary income amidst ever-growing mobility led by the young Indian and rapid growth of the aviation infrastructure ., by end of the decade is likely to be at pole position as the world’s largest aviation market leaving China and USA behind, For the uninitiated, from 72 operational airports in 2014 it increased to 141 in 2022 and is 150 heading into 2024 and sooner will be 200, with 14 cities likely to have dual airports.
The Centre for Asia Pacific Aviation (CAPA) India, an aviation consultancy agency, forecasts that the country’s domestic passenger traffic is likely to rise to 16 crores in FY24 from an estimated 13.75 crore in FY23. By 2029-30, India’s domestic passenger traffic is likely to touch 35 crores. It also projects that by 2043, India could be handling 1.3 billion passengers and operating a commercial fleet of 4,000 aircraft. The industry handled close to 200 million passengers in FY 2023. Indian airlines have more than 1500 aircrafts on order and as per projections of Boeing company Indian carriers are expected to require furthermore than 2,200 aircraft in the next 20 years and will need to train it is going to require us to train 37,000 pilots and 38,000 mechanics over the next 20 years. These are conservative estimates.
Sky is the Limit
And the story just got bigger. The growth potential of aviation in India is much brighter as the sector’s penetration is currently at just 4-5 per cent of India’s population base and demand is rising rapidly. As per Macquarie, discretionary spending in India rose from 13% of household consumption in 2000 to 24% in 2020 and is set to increase by 33% by 2030. By 2047 when the country celebrates 100 years of independence, it is set to become a developed country with substantially higher per capita income. By 2050, as per the United Nations Population Prospect projections, India will be home to 167 crores including 81.5 crore urban dwellers, the latter contributing 80% to GDP. The best of Indian aviation is today a work in progress, and the sky is the limit to its spectacular growth.
End of Article
Subscribe to our daily Newsletter!
Videos





03:53
Urfi Javed Flaunts her Topless Style | Jennifer Mistry's HEARTWARIMNG note for TMKOC

04:45
'World Used Kashmir Against India': What EAM Said On J&K's Art 370| Page From Times Now Archive

02:59
Breaking News: SC Upholds Abrogation Of Article 370 | No Special Status For J&K | Latest Updates

04:35
NC, PDP, And BJP Reacts On Abrogation Of Article 370 | Will Centre Be Vindicated? | Latest News
02:42
Israel Hamas War | Netanyahu Says 'Hamas Is Surrendering' | What's Happening In Gaza? | World News














